 Yamaha MT-03 - Service manual > Electrical components
Yamaha MT-03 - Service manual > Electrical components
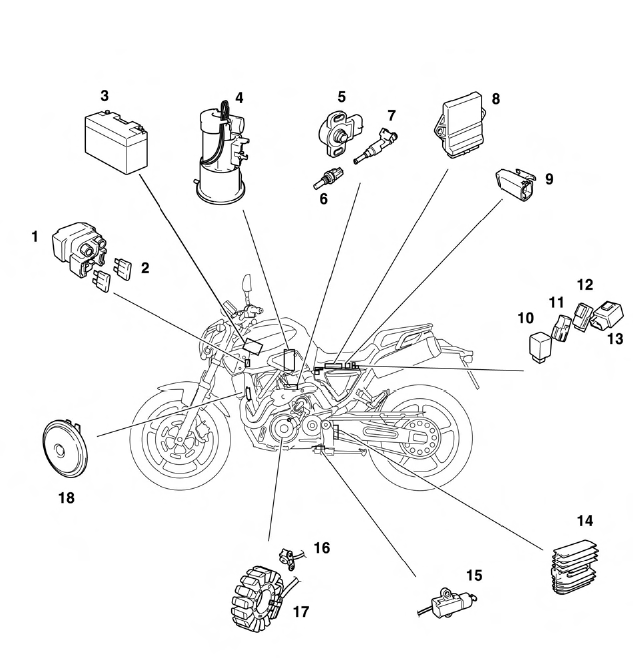
- Starter relay
- Main fuse
- Battery
- Fuel pump
- Throttle position sensor
- Coolant temperature sensor
- Fuel injector
- ECU (electronic control unit)
- Lean angle cut-off switch
- Turn signal/hazard relay
- Headlight relay
- Radiator fan motor relay
- Relay unit
- Rectifier/regulator
- Sidestand switch
- Crankshaft position sensor
- Stator coil
- Horn
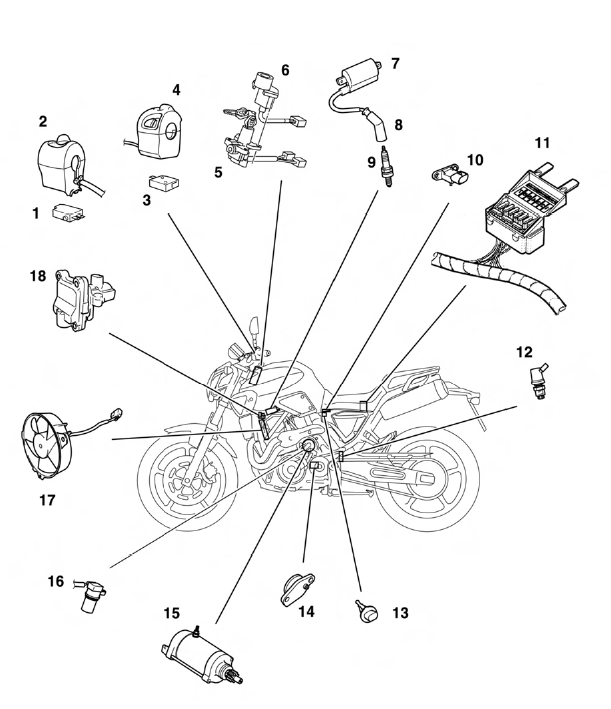
- Front brake light switch
- Right handlebar switch
- Clutch switch
- Left handlebar switch
- Main switch
- Immobilizer unit
- Ignition coil
- Plug cap
- Spark plug
- Intake air pressure sensor
- Fuse box
- Rear brake light switch
- Intake air temperature sensor
- Neutral switch
- Starter motor
- Speed sensor
- Radiator fan motor
- Air induction system solenoid
Checking the switches
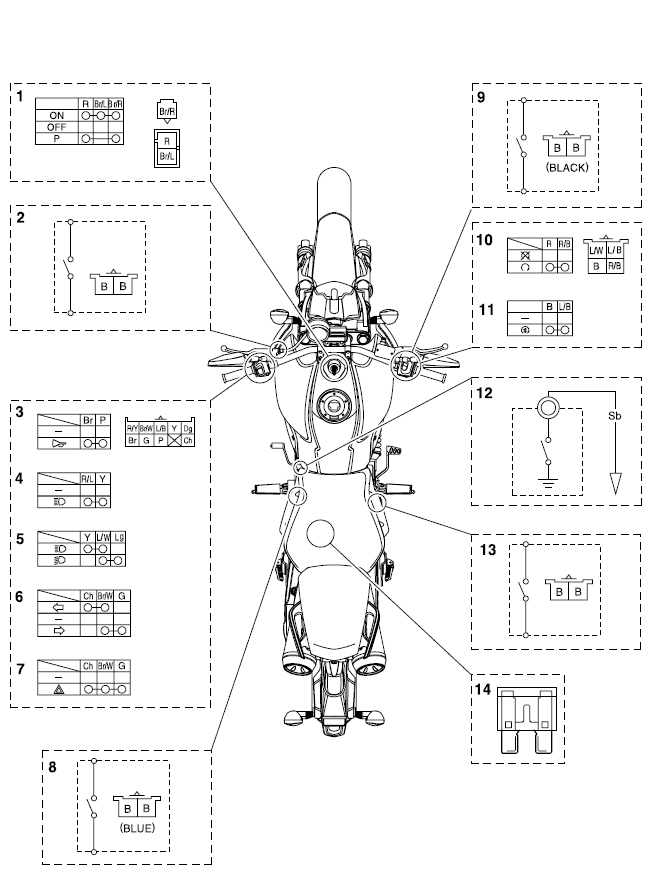
- Main switch
- Clutch switch
- Horn switch
- Pass switch
- Dimmer switch
- Turn signal switch
- Hazard switch
- Sidestand switch
- Front brake light switch
- Engine stop switch
- Start switch
- Neutral switch
- Rear brake light switch
- Fuses
Check each switch for continuity with the pocket tester. If the continuity reading is incorrect, check the wiring connections and if necessary, replace the switch.
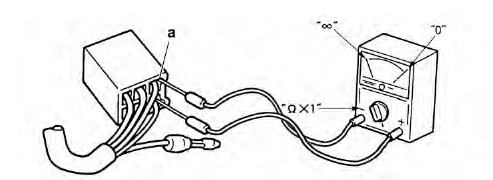
CAUTION:
Never insert the tester probes into the coupler terminal slots "a". Always insert the probes from the opposite end of the coupler, taking care not to loosen or damage the leads.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
NOTE:
- Before checking for continuity, set the pocket tester to "0" and to the "Ω x 1" range.
- When checking for continuity, switch back and forth between the switch positions a few times.
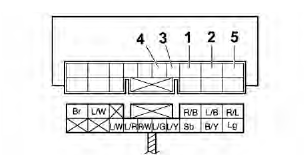
The switches and their terminal connections are illustrated as in the following example of the main switch.
The switch positions "a" are shown in the far left column and the switch lead colors "b" are shown in the top row.
The continuity (i. e., a closed circuit) between switch terminals at a given
switch position is indication
by "  " There is continuity
between red, brown/blue, and brown/red when the switch is set to
"ON" and between red and brown/red when the switch is set to "
" There is continuity
between red, brown/blue, and brown/red when the switch is set to
"ON" and between red and brown/red when the switch is set to "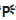 ".
".
Checking the bulbs and bulb sockets
NOTE:
Do not check any of the lights that use LEDs.
Check each bulb and bulb socket for damage or wear, proper connections, and also for continuity between the terminals.
Damage/wear → Repair or replace the bulb, bulb socket or both.
Improperly connected → Properly connect.
No continuity → Repair or replace the bulb, bulb socket or both.
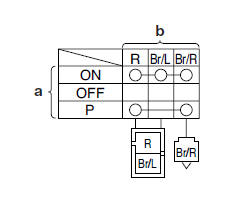
Types of bulbs
The bulbs used on this vehicle are shown in the following illustration.
- Bulbs "a" and "b" are used for the headlights and usually use a bulb holder that must be detached before removing the bulb. The majority of these types of bulbs can be removed from their respective socket by turning them counterclockwise.
- Bulbs "c" are used for turn signal and tail/brake lights and can be removed from the socket by pushing and turning the bulb counterclockwise.
- Bulbs "d" and "e" are used for meter and indicator lights and can be removed from their respective socket by carefully pulling them out.
Checking the condition of the bulbs
The following procedure applies to all of the bulbs.
1. Remove:
- Bulb
WARNING
Since headlight bulbs get extremely hot, keep flammable products and your hands away from them until they have cooled down.
CAUTION:
- Be sure to hold the socket firmly when removing the bulb. Never pull the lead, otherwise it may be pulled out of the terminal in the coupler.
- Avoid touching the glass part of a headlight bulb to keep it free from oil, otherwise the transparency of the glass, the life of the bulb, and the luminous flux will be adversely affected. If a headlight bulb gets soiled, thoroughly clean it with a cloth moistened with alcohol or lacquer thinner.
2. Check:
- Bulb (for continuity) (with the pocket tester) No continuity → Replace.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
NOTE:
Before checking for continuity, set the pocket tester to "0" and to the "Ω x 1" range.
Check each bulb and bulb socket for damage
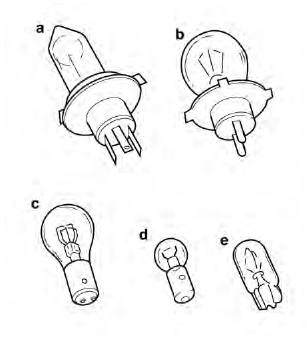
a. Connect the positive tester probe to terminal "1" and the negative tester probe to terminal "2", and check the continuity.
b. Connect the positive tester probe to terminal "1" and the negative tester probe to terminal "3", and check the continuity.
c. If either of the readings indicate no continuity, replace the bulb.
Checking the condition of the bulb sockets
The following procedure applies to all of the bulb sockets.
1. Check:
- Bulb socket (for continuity) (with the pocket tester) No continuity → Replace.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
NOTE:
Check each bulb socket for continuity in the same manner as described in the bulb section; however, note the following.
a. Install a good bulb into the bulb socket.
b. Connect the pocket tester probes to the respective leads of the bulb socket.
c. Check the bulb socket for continuity. If any of the readings indicate no continuity, replace the bulb socket.
Checking the leds
The following procedures applies to all of the LEDs.
1. Check:
- LED (for proper operation) Improper operation → Replace.
a. Disconnect the meter assembly coupler (meter assembly end).
b. Connect two jumper leads "1" from the battery terminals to the respective coupler terminal as shown.
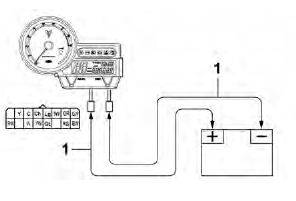
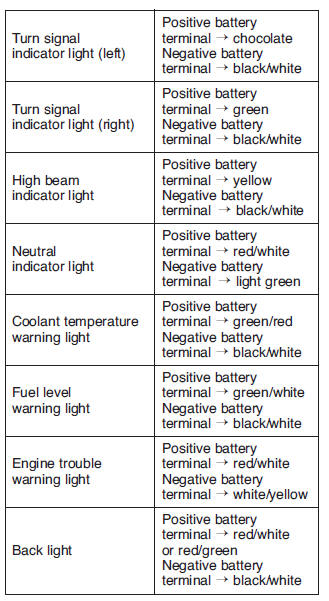
Immobilizer system indicator LED
Connect the pocket tester (kΩ x 1) to the
meter coupler. 
WARNING
- A wire that is used as a jumper lead must have at least the same capacity of the battery lead, otherwise the jumper lead may burn.
- This check is likely to produce sparks, therefore, make sure no flammable gas or fluid is in the vicinity.
CAUTION:
Do not connect the jumper lead (battery voltage) to the terminals (green/blue and black/white) for the immobilizer system indicator light (LED). The LED could be damaged.
c. When the jumper leads are connected to the terminals, the respective LED should illuminate.
Does not light → Replace the meter assembly.
Checking the fuses
The following procedure applies to all of the fuses.
CAUTION:
To avoid a short circuit, always turn the main switch to "OFF" when checking or replacing a fuse.
The main fuse is located under the fuel tank.
The fuse box which contains the fuses for the individual circuits is located under the rider seat.
1. Remove:
- Seats
- Fuel tank
2. Check:
- Fuse
a. Connect the pocket tester to the fuse and check the continuity.
NOTE:
Set the pocket tester selector to "Ω x 1".
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
b. If the pocket tester indicates "∞", replace the fuse.
3. Replace:
- Blown fuse
a. Turn the main switch to "OFF".
b. Install a new fuse of the correct amperage rating.
c. Set on the switches to verify if the electrical circuit is operational.
d. If the fuse immediately blows again, check
the electrical circuit. 
WARNING
Never use a fuse with an amperage rating other than that specified. Improvising or using a fuse with the wrong amperage rating may cause extensive damage to the electrical system, cause the lighting and ignition systems to malfunction and could possibly cause a fire.
4. Install:
- Fuel tank
- Seats
Checking and charging the battery
WARNING
Batteries generate explosive hydrogen gas and contain electrolyte which is made of poisonousand highly caustic sulfuric acid.
Therefore, always follow these preventive measures:
- Wear protective eye gear when handling or working near batteries.
- Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area.
- Keep batteries away from fire, sparks or open flames (e.g., welding equipment, lighted cigarettes).
- DO NOT SMOKE when charging or handling batteries.
- KEEP BATTERIES AND ELECTROLYTE OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
- Avoid bodily contact with electrolyte as it can cause severe burns or permanent eye injury.
FIRST AID IN CASE OF BODILY CONTACT: EXTERNAL
- Skin - Wash with water.
- Eyes - Flush with water for 15 minutes and get immediate medical attention.
INTERNAL
- Drink large quantities of water or milk followed with milk of magnesia, beaten egg or vegetable oil. Get immediate medical attention.
CAUTION:
- This is a sealed battery. Never remove the sealing caps because the balance between cells will not be maintained and battery performance will deteriorate.
- Charging time, charging amperage and
charging voltage for an MF battery are different
from those of conventional batteries.
The MF battery should be charged as explained in the charging method illustrations.
If the battery is overcharged, the electrolyte level will drop considerably.
Therefore, take special care when charging the battery
NOTE:
Since MF batteries are sealed, it is not possible to check the charge state of the battery by measuring the specific gravity of the electrolyte.
Therefore, the charge of the battery has to be checked by measuring the voltage at the battery terminals.
1. Remove:
- Seats
- Fuel tank
- Battery cover
CAUTION:
First, disconnect the negative battery lead "1", and then positive battery lead "2".
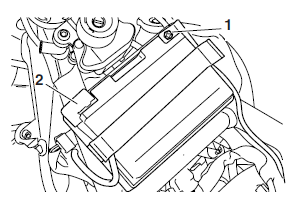
3. Remove:
- Battery band
- Battery
4. Check:
- Battery charge
a. Connect a pocket tester to the battery terminals.
- Positive tester probe → positive battery terminal
- Negative tester probe → negative battery terminal
NOTE:
- The charge state of an MF battery can be checked by measuring its open-circuit voltage (i.e., the voltage when the positive battery terminal is disconnected).
- No charging is necessary when the open-circuit voltage equals or exceeds 12.8 V.
b. Check the charge of the battery, as shown in the charts and the following example.
Example
Open-circuit voltage = 12.0 V
Charging time = 6.5 hours
Charge of the battery = 20-30%
5. Charge:
- Battery (refer to the appropriate charging method)
WARNING
Do not quick charge a battery
CAUTION:
- Never remove the MF battery sealing caps.
- Do not use a high-rate battery charger since it forces a high-amperage current into the battery quickly and can cause bat-tery overheating and battery plate damage.
- If it is impossible to regulate the charging current on the battery charger, be careful not to overcharge the battery.
- When charging a battery, be sure to remove it from the vehicle. (If charging has to be done with the battery mounted on the vehicle, disconnect the negative battery lead from the battery terminal.)
- To reduce the chance of sparks, do not plug in the battery charger until the battery charger leads are connected to the battery.
- Before removing the battery charger lead clips from the battery terminals, be sure to turn off the battery charger.
- Make sure the battery charger lead clips are in full contact with the battery terminal and that they are not shorted. A corroded battery charger lead clip may generate heat in the contact area and a weak clip spring may cause sparks.
- If the battery becomes hot to the touch at any time during the charging process, disconnect the battery charger and let the bat tery cool before reconnecting it. Hot batteries can explode!
- As shown in the following illustration, the open-circuit voltage of an MF battery stabilizes about 30 minutes after charging has been completed. Therefore, wait 30 minutes after charging is completed before measuring the open-circuit voltage.
Charging method using a variable-current (voltage) charger
a. Measure the open-circuit voltage prior to charging.
NOTE:
Voltage should be measured 30 minutes after the engine is stopped.
b. Connect a charger and ammeter to the battery and start charging.
NOTE:
Set the charging voltage at 16-17 V.If the setting is lower, charging will be insufficient. If too high, the battery will be over-charged.
c. Make sure that the current is higher than the standard charging current written on the battery.
NOTE:
If the current is lower than the standard charging current written on the battery, set the charging voltage adjust dial at 20-24 V and monitor the amperage for 3-5 minutes to check the battery.
- Standard charging current is reached Battery is good.
- Standard charging current is not reached Replace the battery.
d. Adjust the voltage so that the current is at the standard charging level.
e. Set the time according to the charging time suitable for the open-circuit voltage.
Refer to "Battery condition checking steps".
f. If charging requires more than 5 hours, it is advisable to check the charging current after a lapse of 5 hours. If there is any change in the amperage, readjust the voltage to obtain the standard charging current.
g. Measure the battery open-circuit voltage after leaving the battery unused for more than 30 minutes.
12.8 V or more --- Charging is complete.
12.7 V or less --- Recharging is required.
Under 12.0 V --- Replace the battery.
Charging method using a constant voltage charger
a. Measure the open-circuit voltage prior to charging.
NOTE:
Voltage should be measured 30 minutes after the engine is stopped.
b. Connect a charger and ammeter to the battery and start charging.
c. Make sure that the current is higher than the standard charging current written on the battery.
NOTE:
If the current is lower than the standard charging current written on the battery, this type of battery charger cannot charge the MF battery.
A variable voltage charger is recommended.
d. Charge the battery until the battery's charging voltage is 15 V.
NOTE:
Set the charging time at 20 hours (maximum).
e. Measure the battery open-circuit voltage after leaving the battery unused for more than 30 minutes.
12.8 V or more --- Charging is complete.
12.7 V or less --- Recharging is required.
Under 12.0 V --- Replace the battery.
6. Install:
- Battery
- Battery band
7. Connect:
- Battery leads (to the battery terminals)
CAUTION:
First, connect the positive battery lead "1", and then the negative battery lead "2".
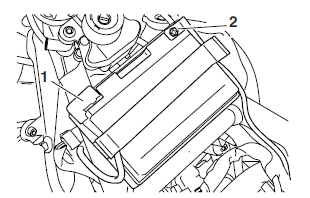
8. Check:
- Battery terminals
- Dirt → Clean with a wire brush. Loose connection → Connect properly.
9. Lubricate:
- Battery terminals
 Recommended lubricant
Dielectric grease
Recommended lubricant
Dielectric grease
10. Install:
- Battery cover
- Fuel tank
- Seats
Checking the relays
Check each switch for continuity with the pocket tester. If the continuity reading is incorrect, replace the relay.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
1. Disconnect the relay from the wire harness.
2. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1) and battery (12 V) to the relay terminal as shown.
Check the relay operation.
Out of specification → Replace.
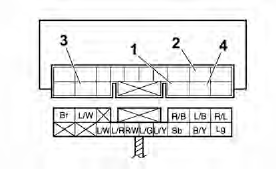
Starter relay
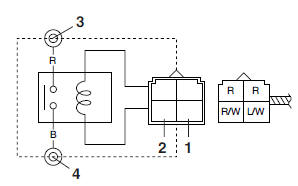
1. Positive battery terminal
2. Negative battery terminal
3. Positive tester probe
4. Negative tester probe
 Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
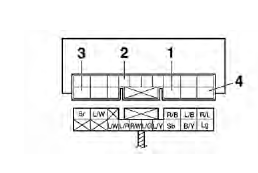
Relay unit (starting circuit cut-off relay)
- Positive battery terminal
- Negative battery terminal
- Positive tester probe
- Negative tester probe
 Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Fuel injection system relay
- Positive battery terminal
- Negative battery terminal
- Positive tester probe
- Negative tester probe
 Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Headlight relay
- Positive battery terminal
- Negative battery terminal
- Positive tester probe
- Negative tester probe
 Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Radiator fan motor relay
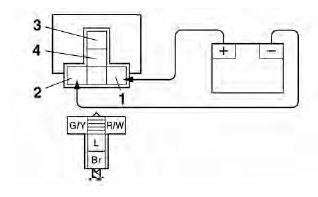
- Positive battery terminal
- Negative battery terminal
- Positive tester probe
- Negative tester probe
 Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Result
Continuity
(between "3" and "4")
Checking the turn signal/hazard relay
1. Check:
- Turn signal/hazard relay input voltage.
Out of specification → The wiring circuit from the main switch to the turn signal/hazard relay coupler is faulty and must be repaired.
 Turn signal/hazard relay input
voltage
DC 12 V
Turn signal/hazard relay input
voltage
DC 12 V
a. Connect the pocket tester (DC 20 V) to the turn signal/hazard relay terminal as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → brown "1"
- Negative tester probe → ground
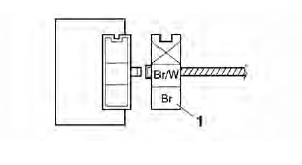
b. Turn the main switch to "ON".
c. Measure the turn signal/hazard relay input voltage.
2. Check:
- Turn signal/hazard relay output voltage.
Out of specification → Replace.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → brown/white "1"
- Negative tester probe → ground
b. Turn the main switch to "ON".
c. Measure the turn signal/hazard relay outputvoltage.
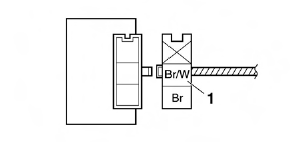
Checking the relay unit (diode)
1. Check:
- Relay unit (diode) Out of specification → Replace.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
NOTE:
The pocket tester and the analog pocket tester readings are shown in the following table.
 Continuity
Positive tester probe →
sky blue "1"
Negative tester probe →
black/yellow "2"
Continuity
Positive tester probe →
sky blue "1"
Negative tester probe →
black/yellow "2"
No continuity
Positive tester probe → black/yellow "2" Negative tester probe → sky blue "1"
Continuity
Positive tester probe → sky blue "1" Negative tester probe → blue/yellow "3"
No continuity
Positive tester probe → blue/yellow "3" Negative tester probe → sky blue "1"
Continuity
Positive tester probe → sky blue "1" Negative tester probe → light green "5"
No continuity
Positive tester probe → light green "5" Negative tester probe → sky blue "1"
Continuity
Positive tester probe → blue/green "4" Negative tester probe → blue/yellow "3"
No continuity
Positive tester probe → blue/yellow "3" Negative tester probe → blue/green "4"
a. Disconnect the relay unit coupler from the wire harness.
b. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1) to the relay unit terminal as shown.
c. Check the relay unit (diode) for continuity.
d. Check the relay unit (diode) for no continuity.
Checking the spark plug cap
1. Check:
- Spark plug cap resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
 Resistance
10.0 kΩ at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
Resistance
10.0 kΩ at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
a. Remove the spark plug cap from the spark plug lead.
b. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1k) to the spark plug cap as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
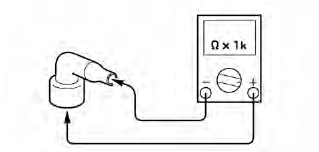
c. Measure the spark plug cap resistance.
Checking the ignition coil
1. Check:
- Primary coil resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
 Primary coil resistance
3.4-4.6 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
Primary coil resistance
3.4-4.6 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
a. Disconnect the ignition coil connectors from the ignition coil terminals.
b. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1) to the ignition coil as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → red/black "1"
- Negative tester probe → orange "2"
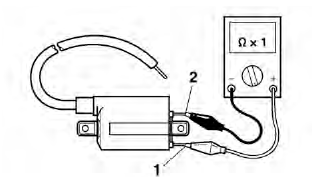
c. Measure the primary coil resistance.
2. Check:
- Secondary coil resistance.
Out of specification → Replace.
 Secondary coil resistance
10.4-15.6 kΩ at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
Secondary coil resistance
10.4-15.6 kΩ at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
a. Disconnect the spark plug cap from the ignition coil.
b. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1k) to the ignition coil as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → red/black "1"
- Negative tester probe → spark plug lead "2"
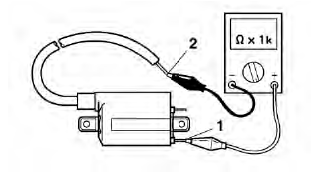
c. Measure the secondary coil resistance.
Checking the ignition spark gap
1. Check:
- Ignition spark gap
Out of specification → Perform the ignition system troubleshooting, starting with step 5.
 Minimum ignition spark gap
6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Minimum ignition spark gap
6.0 mm (0.24 in)
NOTE:
If the ignition spark gap is within specification, the ignition system circuit is operating normally.
a. Disconnect the spark plug cap "2" from the spark plug.
b. Connect the ignition checker "1" as shown.
 Ignition checker
90890-06754
Ignition checker
90890-06754
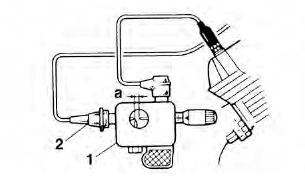
2. Spark plug cap
c. Turn the main switch to "ON" and engine
stop switch to " ".
".
d. Measure the ignition spark gap "a".
e. Crank the engine by pushing the start switch
" " and gradually increase the spark
gap
until a misfire occurs.
" and gradually increase the spark
gap
until a misfire occurs.
Checking the crankshaft position sensor
1. Disconnect:
- Crankshaft position sensor coupler (from the wire harness)
2. Check:
- Crankshaft position sensor resistance
Out of specification → Replace the crankshaft position sensor.
 Crankshaft position sensor
resistance
192-288 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)/
blue/yellow-green/white
Crankshaft position sensor
resistance
192-288 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)/
blue/yellow-green/white
a. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 100) to the crankshaft position sensor coupler as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → blue/yellow "1"
- Negative tester probe → green/white "2"
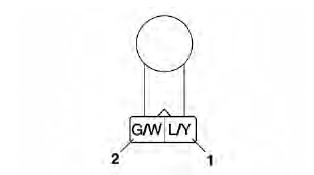
b. Measure the crankshaft position sensor resistance.
Checking the lean angle cut-off switch
1. Remove:
- Lean angle cut-off switch
2. Check:
- Lean angle cut-off switch output voltage Out of specification → Replace.
 Lean angle cut-off switch
output
voltage
Lean angle cut-off switch
output
voltage
Less than 65º: 0.4-1.4 V
More than 65º: 3.7-4.4 V
a. Connect the lean angle cut-off switch coupler to the lean angle cut-off switch.
b. Connect the pocket tester (DC 20 V) to the lean angle cut-off switch coupler as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → yellow/green "1"
- Negative tester probe → black/blue "2"
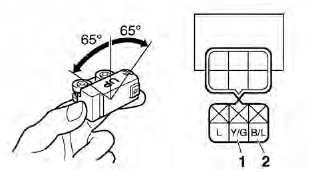
c. Turn the lean angle cut-off switch to 65º.
d. Measure the lean angle cut-off switch output voltage.
Checking the stator coil
1. Disconnect:
- Stator coil coupler (from the wire harness)
2. Check:
- Stator coil resistance
Out of specification → Replace the stator assembly.
 Stator coil resistance
0.224-0.336 Ω at 20 ºC (38 ºF)
Stator coil resistance
0.224-0.336 Ω at 20 ºC (38 ºF)
a. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1) to the stator coil coupler as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → white "1"
- Negative tester probe → white "2"
- Positive tester probe → white "1"
- Negative tester probe → white "3"
b. Measure the stator coil resistance.
Checking the horn
1. Check:
- Horn resistance
Out of specification →Replace.
 Coil resistance
1.15-1.25 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
Coil resistance
1.15-1.25 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
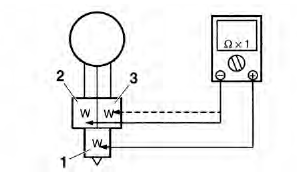
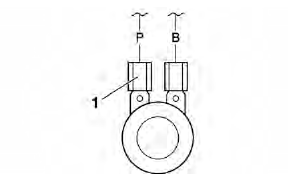
a. Disconnect the horn leads from the horn terminals.
b. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1) to the horn terminals.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → horn terminal
- Negative tester probe → horn terminal
c. Measure the horn resistance.
2. Check:
- Voltage
a. Disconnect the horn leads from the horn terminals.
b. Connect the pocket tester (DC 20 V) to the horn leads.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → pink "1"
- Negative tester probe → ground
c. Set the main switch to "ON".
d. Push the horn switch.
e. Measure the voltage (DC 12 V) of pink at the horn terminal.
3. Check:
- Horn sound.
Faulty sound → Replace the horn.
a. Disconnect the horn leads from the horn terminals.
b. Connect a battery (12 V) to the horn terminals.
Checking the coolant temperature sensor
1. Remove:
- Coolant temperature sensor (from the engine)
WARNING
- Handle the coolant temperature sensor with special care.
- Never subject the coolant temperature sensor to strong shocks. If the coolant temperature sensor is dropped, replace it.
2. Check:
- Coolant temperature sensor resistance Out of specification → Replace.
 Coolant temperature sensor
resistance.
Coolant temperature sensor
resistance.
2.28-2.63 kΩ at 20 ºC (68 ºF) 0.305-0.331 kΩ at 80 ºC (176 ºF) 0.138-0.145 kΩ at 110 ºC (230 ºF)
a. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1k) to the coolant temperature sensor terminal as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
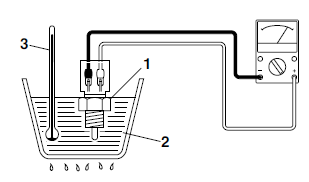
b. Immerse the coolant temperature sensor "1" in a container filled with water "2".
NOTE:
Make sure that the coolant temperature sensor terminals do not get wet.
c. Place a thermometer "3" in the water.
d. Slowly heat the water, then let it cool down to the specified temperature.
e. Measure the coolant temperature sensor resistance.
3. Install:
- Coolant temperature sensor
 Coolant temperature sensor
18 Nm (1.8 m*kg, 13 ft*lb)
Coolant temperature sensor
18 Nm (1.8 m*kg, 13 ft*lb)
Checking the fuel sender
This model is equipped with a self-diagnosis device for the fuel sender circuit. If the fuel sender circuit is defective, the following cycle will be repeated until the malfunction is corrected.
- The fuel level warning light will flash four times and then go off for 3.0 seconds if the fuel sender circuit is in short circuit.
- The fuel level warning light will flash eight times and then go off for 3.0 seconds if the fuel sender circuit is interrupted or the coupler disconnected.
1. Remove:
- Fuel tank
2. Disconnect:
- Fuel pump coupler
- Fuel sender coupler.
(from the wire harness)
3. Remove:
- Fuel pump.
(from the fuel tank)
4. Check:
- Fuel sender resistance.
Out of specification → Replace the fuel pump assembly.
 Fuel sender resistance
1.35-1.65 kΩ at 25 ºC (77 ºF)
Fuel sender resistance
1.35-1.65 kΩ at 25 ºC (77 ºF)
a. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1k) to the fuel sender terminal as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → green/white "1"
- Negative tester probe → black "2"
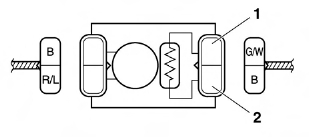
b. Measure the fuel sender resistance.
Checking the speed sensor
1. Check:
Speed sensor output voltage.
Out of specification → Replace.
 Output voltage reading cycle
0.6 V to 4.8 V to 0.6 V to 4.8 V
Output voltage reading cycle
0.6 V to 4.8 V to 0.6 V to 4.8 V
a. Connect the pocket tester (DC 20 V) to the speed sensor coupler (wire harness side) as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → pink "1"
- Negative tester probe → black/white "2"
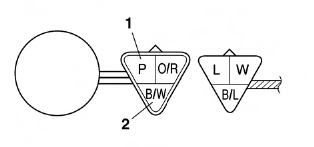
b. Turn the main switch to "ON".
c. Elevate the rear wheel and slowly rotate it.
d. Measure the voltage (DC 5V) of pink and black/white. With each full rotation of the rear wheel, the voltage reading should cycle from 0.6 V to 4.8 V to 0.6 V to 4.8 V.
Checking the throttle position sensor
1. Remove:
- Throttle position sensor (from the throttle body)
2. Check:
- Throttle position sensor maximum resistance Out of specification → Replace the throttle position sensor.
 Resistance
4.0-6.0 kΩ/blue-black/blue
Resistance
4.0-6.0 kΩ/blue-black/blue
a. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 1k) to the throttle position sensor terminal as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → blue "1"
- Negative tester probe → black/blue "2"
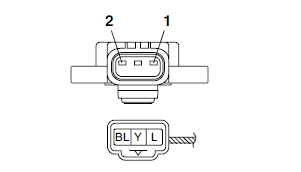
b. Measure the throttle position sensor maximum resistance.
3. Install:
- Throttle position sensor
NOTE:
When installing the throttle position sensor, adjust its angle properly.
Checking the fuel pump
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and under certain circumstances there can be a danger of an explosion or fire. Be extremely careful and note the following points:
- Stop the engine before refueling.
- Do not smoke, and keep away from open flames, sparks, or any other source of fire.
- If you do accidentally spill gasoline, wipe it up immediately with dry rags.
- If gasoline touches the engine when it is hot, a fire may occur. Therefore, make sure the engine is completely cool before performing the following test.
1. Remove:
- Fuel tank
2. Disconnect:
- Fuel pump coupler
- Fuel sender coupler (from the wire harness)
3. Check:
- Fuel pump operation
Faulty/rough movement → Replace.
a. Fill the fuel tank.
b. Put the end of the fuel hose "1" into an open container.
c. Connect the battery (DC 12 V) to the fuel pump terminal as shown.
- Positive battery lead → red/blue "1"
- Negative battery lead → black "2"
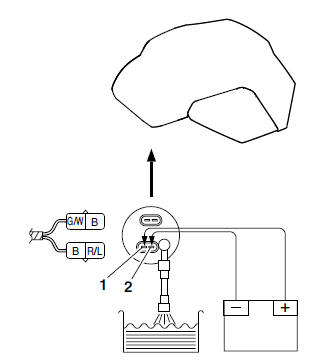
d. Check the fuel pump operation.
Checking the intake air pressure sensor
1. Check:
- Intake air pressure sensor output voltage Out of specification → Replace.
 Intake pressure sensor output
voltage
3.4-3.8 V
Intake pressure sensor output
voltage
3.4-3.8 V
a. Connect the pocket tester (DC 20 V) to the intake air pressure sensor coupler as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → pink/white "1"
- Negative tester probe → black/blue "2"
b. Turn the main switch to "ON".
c. Measure the intake air pressure sensor output voltage.
Checking the intake air temperature sensor
1. Remove:
- Intake air temperature sensor (from the air filter case)
WARNING
- Handle the intake air temperature sensor with special care.
- Never subject the intake air temperature sensor to strong shocks. If the intake air temperature sensor is dropped, replace it.
2. Check:
- Intake air temperature sensor resistance Out of specification → Replace.
 Intake air temperature sensor
resistance
2.21-2.69 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
Intake air temperature sensor
resistance
2.21-2.69 Ω at 20 ºC (68 ºF)
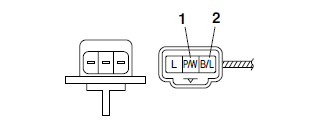
a. Connect the pocket tester (Ω x 100) to the intake air temperature sensor terminal as shown.
 Pocket tester
90890-03112
Pocket tester
90890-03112
- Positive tester probe → brown/white "1"
- Negative tester probe → black/blue "2"
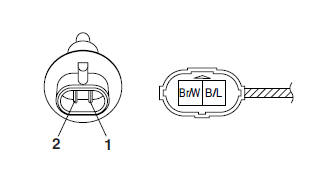
b. Measure the intake air temperature sensor resistance.
Checking the radiator fan motor
1. Check:
- Radiator fan motor.
Faulty/rough movement → Replace.
a. Disconnect the radiator fan motor coupler from the wire harness.
b. Connect the battery (DC 12 V) as shown.
- Positive tester probe → red "1
- Negative tester probe → black "2"
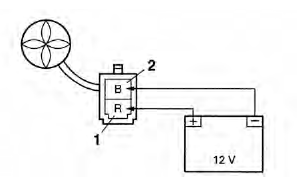
c. Check the radiator fan motor movement.
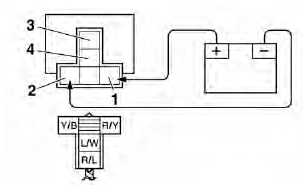
Checking the starter motor
1. Check:
- Starter motor
a. Connect the positive battery terminal "1" and starter motor lead "2" with a jumper lead "3".
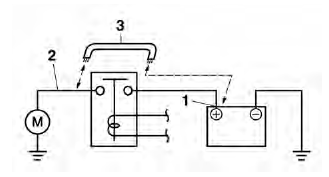
WARNING
- A wire that is used as a jumper lead must have at least the same capacity or more as that of the battery lead, otherwise the jumper lead may burn.
- This check is likely to produce sparks, therefore make sure nothing flammable is in the vicinity.
b. Check the radiator fan motor movement.
See also:
 Yamaha MT-03 - Service manual > Immobilizer system
Yamaha MT-03 - Service manual > Immobilizer system
Circuit diagram 4. Main switch 7. Battery 8. Main fuse
 Yamaha MT-03 - Service manual > Troubleshooting
Yamaha MT-03 - Service manual > Troubleshooting
General information NOTE: The following guide for troubleshooting does not cover all the possible causes of trouble. It should be helpful, however, as a guide to basic troubleshooting. Refer to the relative procedure in this manual for checks, adjustments, and replacement of parts.

 Benelli Imperiale 400
Benelli Imperiale 400 BMW F900XR
BMW F900XR Honda CB500X
Honda CB500X KTM 390 Adventure
KTM 390 Adventure Triumph Street Triple S
Triumph Street Triple S Yamaha MT-03
Yamaha MT-03 Kawasaki Z400
Kawasaki Z400 Triumph Street Triple S
Triumph Street Triple S Yamaha MT-03
Yamaha MT-03