 Triumph Street Triple S - Service manual > Engine Management System
Triumph Street Triple S - Service manual > Engine Management System
System Description
The Daytona 675, Street Triple and Street Triple R models are fitted with an electronic engine management system which encompasses control of both ignition and fuel delivery. The electronic control module (ECM) draws information from sensors positioned around the engine, cooling and air intake systems and precisely calculates ignition advance and fueling requirements for all engine speeds and loads.
In addition, the system has an on-board diagnostic function.
System Sensors
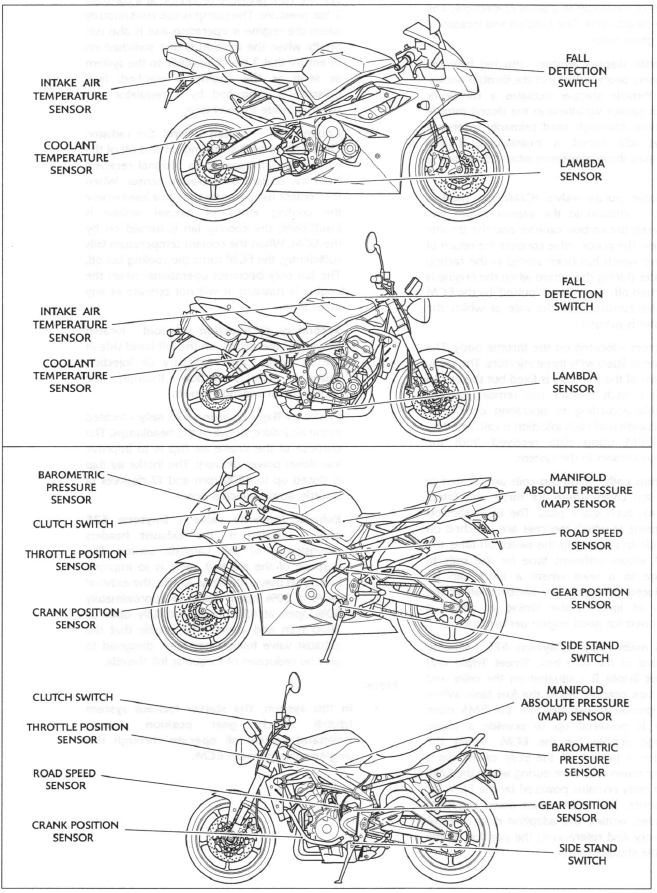
- Intake air temperature sensor - situated in the top of the airbox. As the density of the air (and therefore the amount of oxygen available to ignite the fuel) changes with temperature, an intake air temperature sensor is fitted. Changes in air temperature (and therefore air density) are compensated for by adjusting the amount of fuel injected to a level consistent with clean combustion and low emissions.
- Barometric pressure sensor - Daytona 675 - situated behind the cockpit and below the instrument pack. Street Triple and Street Triple R - situated on the rear subframe, forward of the rear light unit. The barometric pressure sensor measures atmospheric air pressure. With this information, the amount of fuel injected is adjusted to suit the prevailing conditions.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor - situated to the left side of the airbox, connected to each of the three throttle bodies by equal length tubes. The MAP sensor provides information to the ECM which is used at shallow throttle angles (very small throttle openings) to provide accurate engine load indications to the ECM. This degree of engine load accuracy allows the ECM to make very small adjustments to fuel and ignition which would otherwise not be possible from throttle angle data alone.
- Clutch switch - situated on the clutch lever.
The clutch must be pulled in for the starter motor to operate. - Crankshaft position sensor - situated in the alternator cover. The
crankshaft position sensor detects movement of teeth attached to the
alternator rotor.
The toothed rotor gives a reference point from which the actual crankshaft position is calculated. The crankshaft position sensor information is used by the ECM to determine engine speed and crankshaft position in relation to the point where fuel is injected and ignition of the fuel occurs. - Engine coolant temperature sensor - situated at the rear of the cylinder
head.
Coolant temperature information, received by the ECM, is used to optimise fueling at all engine temperatures and to calculate hot and cold start fueling requirements. - Throttle position sensor - situated at the right end of the throttle
body. Used to relay throttle position information to the ECM.
Throttle opening angle is used by the ECM to determine fueling and ignition requirements for all throttle positions. - Road speed sensor - situated in the upper crankcase, in front of the
engine breather.
The road speed sensor provides the ECM with data from which road speed is calculated and displayed on the speedometer. - Lambda sensor - situated in the exhaust header system upstream of the catalyst. The lambda sensor constantly feeds information to the ECM on the content of the exhaust gases. Based on this information, adjustments to the air/fuel ratio are made.
- Side stand switch - situated at the top of the sidestand leg. If the sidestand is in the down position, the engine will not run unless the transmission is in neutral.
- Gear position sensor - situated in the upper crankcase, behind the gearbox output sprocket cover, on the left hand side of the engine. The gear position sensor provides the ECM with selected gear information. This is used to prevent the engine from starting if the transmission is in gear. The sensor also provides information to the gear position indicator and the neutral lamp in the instruments.
- Fall detection switch - Daytona 675 - situated below the instrument pack. Street Triple and Street Triple R - situated on the relay and fuse box bracket below the fuel tank. The fall detection switch will detect if the motorcycle is on its side and will cut power to the ECM immediately. This prevents the engine from running and the fuel pump from delivering fuel. In the event of a fall, the switch is reset by returning the bike to an upright position and switching the ignition off then back on again.
Sensor Locations
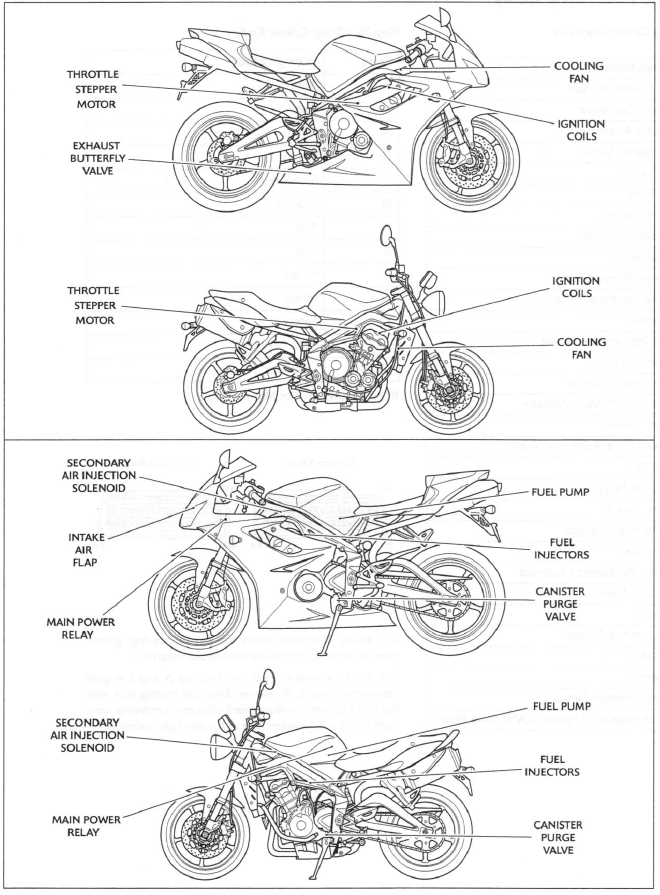
System Actuators
In response to signals received from the sensors, the ECM controls and directs messages to a series of electronic and electro-mechanical actuators. The function and location of the actuators is given below.
- Throttle stepper motor - situated between cylinders two and three of the
throttle bodies.
The throttle stepper actuates a cam/lever which causes variations in the closed throttle position. Although used primarily to ensure target idle speed is maintained, it also increases throttle opening when the engine is cold. - Canister purge valve (California models only) - situated in the vapour return line between the carbon canister and the throttle bodies. The purge valve controls the return of vapour which has been stored in the carbon canister during the period when the engine is switched off. The valve is 'pulsed' by the ECM to give control over the rate at which the canister is purged.
- Injectors - located on the throttle body. The engine is fitted with
three injectors. The spray pattern of the injectors is fixed but the length
of time each injector can remain open is variable according to operating
conditions.
The duration of each injection is calculated by the ECM using data received from the various sensors in the system. - Ignition coils - plug-top coils are located in the cam cover. There are three coils fitted, one for each spark plug. The ECM controls the point at which the coils are switched on and off. In calculating the switch-on time, the ECM allows sufficient time for the coils to charge to a level where a spark can be produced. The coils are switched off at the point of ignition, the timing of which is optimised for good engine performance.
- EMS main relay - Daytona 675 - situated forward of the fuse box. Street Triple and Street Triple R - situated on the relay and fuse box bracket below the fuel tank. When the ignition is switched on, the EMS main relay is powered up to provide a stable voltage supply for the ECM. When the ignition is turned off, the ECM carries out a power down sequence during which the EMS main relay remains powered by the ECM for 1 minute. The ECM power down sequence includes: writing the adaption data to ECM memory and referencing the position of the throttle stepper motor.
- Fuel pump - located inside the fuel tank. The electric pump delivers fuel into the fuel system, via a pressure regulator, at a constant 3 bar pressure. The pump is run continuously when the engine is operating and is also run briefly when the ignition is first switched on to ensure that 3 bar is available to the system as soon as the engine is cranked. Fuel pressure is controlled by a regulator also situated inside the fuel tank.
- Cooling fan - located behind the radiator.
The ECM controls switching on and off of the cooling fan in response to a signal received from the coolant temperature sensor. When the coolant temperature rises to a level where the cooling effect of natural airflow is insufficient, the cooling fan is turned on by the ECM. When the coolant temperature falls sufficiently, the ECM turns the cooling fan off.
The fan only becomes operational when the engine is running. It will not operate at any other time. - Secondary air injection solenoid - located forward of the airbox, on the left hand side of the air intake. The secondary air injection solenoid controls airflow through the secondary air injection system.
- Intake air flap - Daytona 675 only - located in the air intake, between the headlamps. The purpose of the intake air flap is to improve low down power delivery. The intake air flap is closed up to 4500 rpm and 12 degrees of throttle, above which it opens.
- Exhaust butterfly valve - Daytona 675 only - located in the exhaust headers downstream of the Lambda sensor. The purpose of the exhaust valve is to improve low down power delivery. At idle, the exhaust valve is 30% open, rising to approximately 50% open at 4500 rpm, and fully open at 7000 rpm and above. The profile that the exhaust valve follows has been designed to give no reduction of torque at full throttle.
Note:
- In this system, the starter lockout system (clutch switch, gear position sensor, sidestand switch) all operate through the engine management ECM.
Actuator Locations
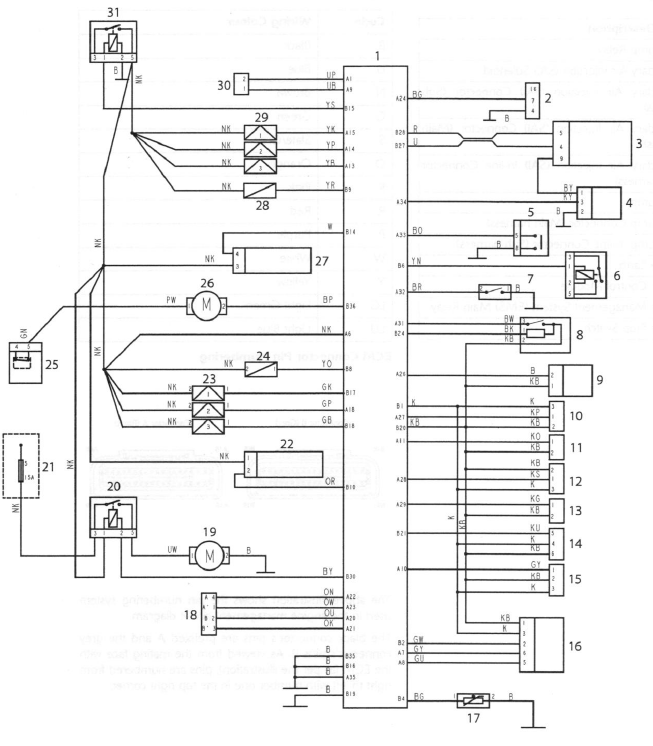
Engine Management Circuit Diagram - Daytona 675 - up to VIN 300525 - without the Fuel Pump Relay
Key To Wiring Circuit Diagram
- Engine Control Module
- Diagnostic Connector
- Instrument Assembly
- Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Clutch Switch
- Starter Relay
- Sidestand Switch
- Gear Position Sensor
- Lambda Sensor
- Barometric Pressure Sensor
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor
- MAP Sensor
- Coolant Temperature Sensor
- Fall Detection Switch
- Throttle Position Sensor
- Exhaust Butterfly Valve Actuator
- Low Fuel Sensor
- Idle Speed Control Stepper Motor
- Cooling Fan
- Cooling Fan Relay
- Fuse Box (fuse 5)
- Intake Air Flap Solenoid
- Ignition Coils
- Secondary Air Injection Solenoid
- Engine Stop Switch
- Fuel Pump
- Heated Lambda Sensor
- Purge Valve
- Fuel Injectors
- Crankshaft Position Sensor
- Engine Management System (EMS) Main Relay
Key To Wiring Colour Codes
B Black
U Blue
N Brown
G Green
S Slate/Grey
O Orange
K Pink
R Red
P Purple
W White
Y Yellow
LG Light Green
LU Light Blue
ECM Connector Pin Numbering
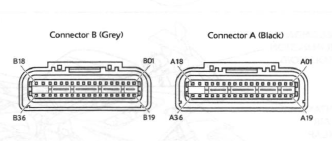
The above illustration shows the pin numbering system used in the engine management circuit diagram.
The black connector's pins are prefixed A and the grey connector's pins B. As viewed from the mating face with the ECM (as per the illustration), pins are numbered from right to left with number one in the top right corner.
Fuel Pump Circuit Diagram - Daytona 675 - from VIN 300526 to VIN 323544 - with the Fuel Pump Relay
Key To Wiring Circuit Diagram
- Fuel Pump Relay
- Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Solenoid
- Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Connector (Sub harness)
- Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Connector (Main harness)
- Secondary Air Injection (SAD In-line Connector (Sub harness)
- Fuel Pump
- Fuel Pump Connector (Main harness)
- Fuel Pump In-line Connector (Sub harness)
- Engine Earth
- Engine Control Module
- Engine Management System (EMS) Main Relay
- Engine Stop Switch
Key To Wiring Colour Codes
B Black
U Blue
N Brown
G Green
S Slate/Grey
O Orange
K Pink
R Red
P Purple
W White
Y Yellow
LG Light Green
LU Light Blue
ECM Connector Pin Numbering
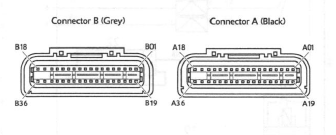
The above illustration shows the pin numbering system used in the engine management circuit diagram.
The black connector's pins are prefixed A and the grey connector's pins B. As viewed from the mating face with the ECM (as per the illustration), pins are numbered from right to left with number one in the top right corner.
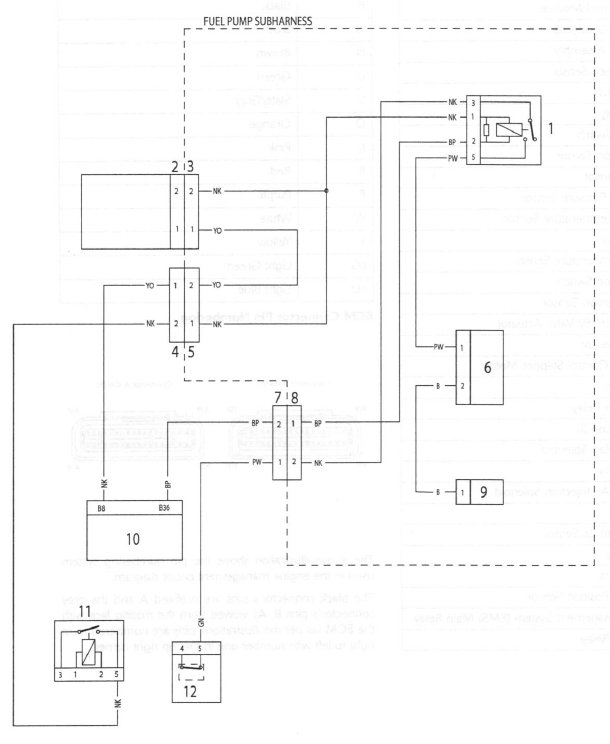
Circuit Diagram - Engine Management System - Daytona 675 - from VIN 323545 to VIN 381274
Key To Wiring Circuit Diagram
- Engine Control Module
- Diagnostic Connector
- Instrument Assembly
- Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Clutch Switch
- Starter Relay
- Sidestand Switch
- Gear Position Sensor
- Lambda Sensor
- Barometric Pressure Sensor
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor
- MAP Sensor
- Coolant Temperature Sensor
- Fall Detection Switch
- Throttle Position Sensor
- Exhaust Butterfly Valve Actuator
- Low Fuel Sensor
- Idle Speed Control Stepper Motor
- Cooling Fan
- Cooling Fan Relay
- Fuse Box (fuse 5)
- Intake Air Flap Solenoid
- Ignition Coils
- Secondary Air Injection Solenoid
- Fuel Pump
- Heated Lambda Sensor
- Purge Valve
- Fuel Injectors
- Crankshaft Position Sensor
- Engine Management System (EMS) Main Relay
- Fuel Pump Relay
Key To Wiring Colour Codes
B Black
U Blue
N Brown
G Green
S Slate/Grey
O Orange
K Pink
R Red
P Purple
W White
Y Yellow
LG Light Green
LU Light Blue
ECM Connector Pin Numbering
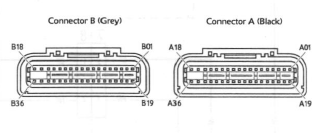
The above illustration shows the pin numbering system used in the engine management circuit diagram.
The black connector's pins are prefixed A and the grey connector's pins B. As viewed from the mating face with the ECM (as per the illustration), pins are numbered from right to left with number one in the top right corner.
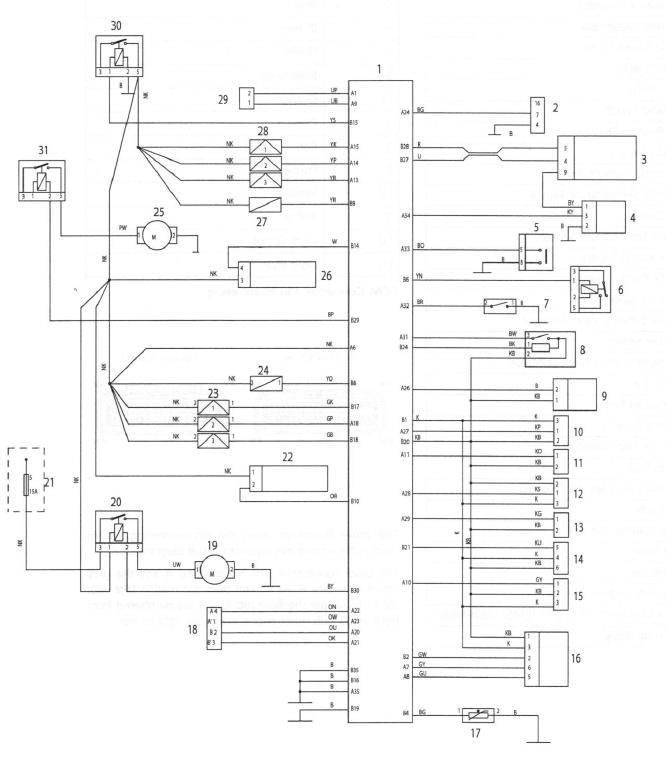
Circuit Diagram - Engine Management System - Daytona 675 - from VIN 381275
Key To Wiring Circuit Diagram
- Engine Control Module
- Diagnostic Connector
- Instrument Assembly
- Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Clutch Switch
- Starter Relay
- Sidestand Switch
- Gear Position Sensor
- Lambda Sensor
- Barometric Pressure Sensor
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor
- MAP Sensor
- Coolant Temperature Sensor
- Fall Detection Switch
- Throttle Position Sensor
- Accessory quickshifter
- Exhaust Butterfly Valve Actuator
- Low Fuel Sensor
- Idle Speed Control Stepper Motor
- Cooling Fan
- Cooling Fan Relay
- Fuse Box (fuse 5)
- Intake Air Flap Solenoid
- Ignition Coils
- Secondary Air Injection Solenoid
- Fuel Pump
- Heated Lambda Sensor
- Purge Valve
- Fuel Injectors
- Crankshaft Position Sensor
- Engine Management System (EMS) Main Relay
- Fuel Pump Relay
Key To Wiring Colour Codes
B Black
U Blue
N Brown
G Green
S Slate/Grey
O Orange
K Pink
R Red
P Purple
W White
Y Yellow
LG Light Green
LU Light Blue
ECM Connector Pin Numbering
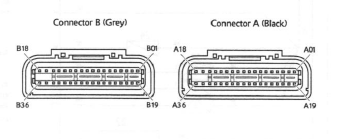
The above illustration shows the pin numbering system used in the engine management circuit diagram.
The black connector's pins are prefixed A and the grey connector's pins B. As viewed from the mating face with the ECM (as per the illustration), pins are numbered from right to left with number one in the top right corner.
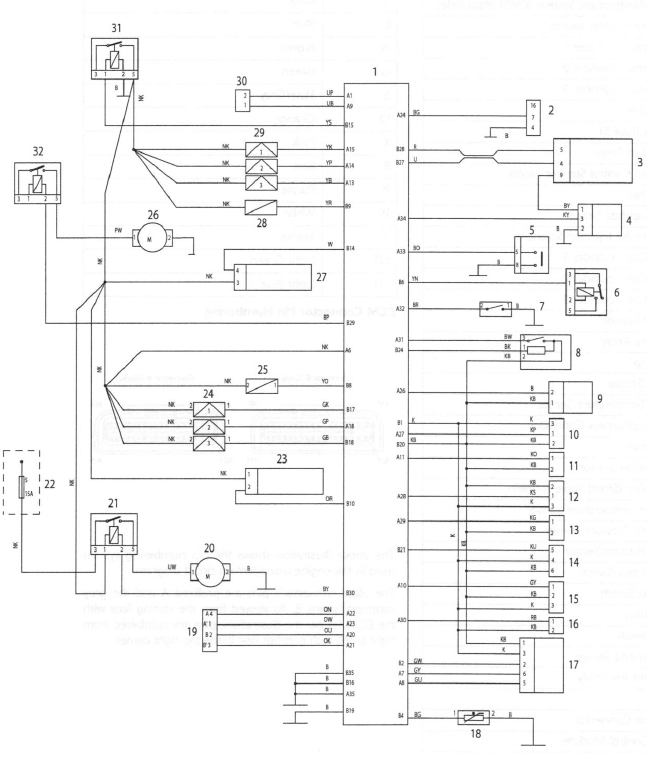
Engine Management Circuit Diagram - Street Triple and Street Triple R
Key To Wiring Circuit Diagram
- Engine Management System (EMS) Main Relay
- Crankshaft Position Sensor
- Fuel Injector - cylinder 1
- Fuel Injector - cylinder 2
- Fuel Injector - cylinder 3
- Purge Valve
- Fuse Box (fuse 5)
- Cooling Fan Relay
- Idle Speed Control Stepper Motor
- Cooling Fan
- Heated Lambda Sensor
- Secondary Air Injection Solenoid
- Ignition Coil - cylinder 1
- Ignition Coil - cylinder 2
- Ignition Coil - cylinder 3
- Low Fuel Sensor
- Fuel Pump Relay
- Fuel Pump
- Lambda Sensor
- Coolant Temperature Sensor
- Engine Subharness Connector
- MAP Sensor
- Gear Position Sensor
- Quickshifter (Street Triple R only)
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor
- Barometric Pressure Sensor
- Throttle Position Sensor
- Fall Detection Switch
- Sidestand Switch
- Starter Relay
- Clutch Switch
- Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Instrument Assembly
- Alarm
- Diagnostic Connector
- Engine Control Module
Key To Wiring Colour Codes
B Black
U Blue
N Brown
G Green
S Slate/Grey
O Orange
K Pink
R Red
P Purple
W White
Y Yellow
LG Light Green
LU Light Blue
ECM Connector Pin Numbering
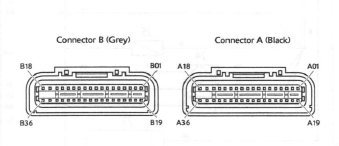
The above illustration shows the pin numbering system used in the engine management circuit diagram.
The black connector's pins are prefixed A and the grey connector's pins B. As viewed from the mating face with the ECM (as per the illustration), pins are numbered from right to left with number one in the top right corner.
See also:
 Triumph Street Triple S - Service manual > Fuel Requirements
Triumph Street Triple S - Service manual > Fuel Requirements
Fuel Requirements - all countries except USA Outside of America, Daytona 675 must be run on 95 RON (or higher) unleaded fuel, and Street Triple and Street Triple R must be run on 91 RON (or higher) unleaded fuel.
 Triumph Street Triple S - Service manual > System Diagnostics
Triumph Street Triple S - Service manual > System Diagnostics
The engine management system has an on-board diagnostics feature which allows service technicians to retrieve stored data from the ECM using the Triumph diagnostic software. Full details of the Triumph diagnostic software operation and how to interpret the results are given in the Triumph Diagnostic Tool User Guide.

 Benelli Imperiale 400
Benelli Imperiale 400 BMW F900XR
BMW F900XR Honda CB500X
Honda CB500X KTM 390 Adventure
KTM 390 Adventure Triumph Street Triple S
Triumph Street Triple S Yamaha MT-03
Yamaha MT-03 Kawasaki Z400
Kawasaki Z400 Triumph Street Triple S
Triumph Street Triple S Yamaha MT-03
Yamaha MT-03